Field recording
Alexander Kroupa & Christoph Häuser (MfN)
|
KEY RESOURCES |
|---|
| Download the full report on mobile devices |
A review of mobile apps for biodiversity
The sharp acceleration of technological development has resulted in a wide variety of mobile phones and in particular the performance of the current generation of ‘smartphones’ is astonishing in an historical perspective. Consequently the transition between mobile phones and personal computers has become more and more blurred, effectively merging netbooks, tablet PCs and smartphones.
This trend can also be observed in the development of the relevant software, commonly known as 'apps', and in many cases standard PC software is also available for mobile devices, too. The high competition between companies for their operating systems, the apps they support and the huge community of developers of free or low-cost apps for open-source systems, is driving innovative mobile tools forward in many areas. Thus, there are several apps available for biodiversity, for instance those providing information about species or taxa, determination aids (keys) and even tools for recording observations including additional (e.g. geospatial) information to populate a database directly from the field. We have produced a report summarising the general advantages of modern mobile devices, categorising and summarising the capabilities of the most important biodiversity apps.
 |
 |
 |
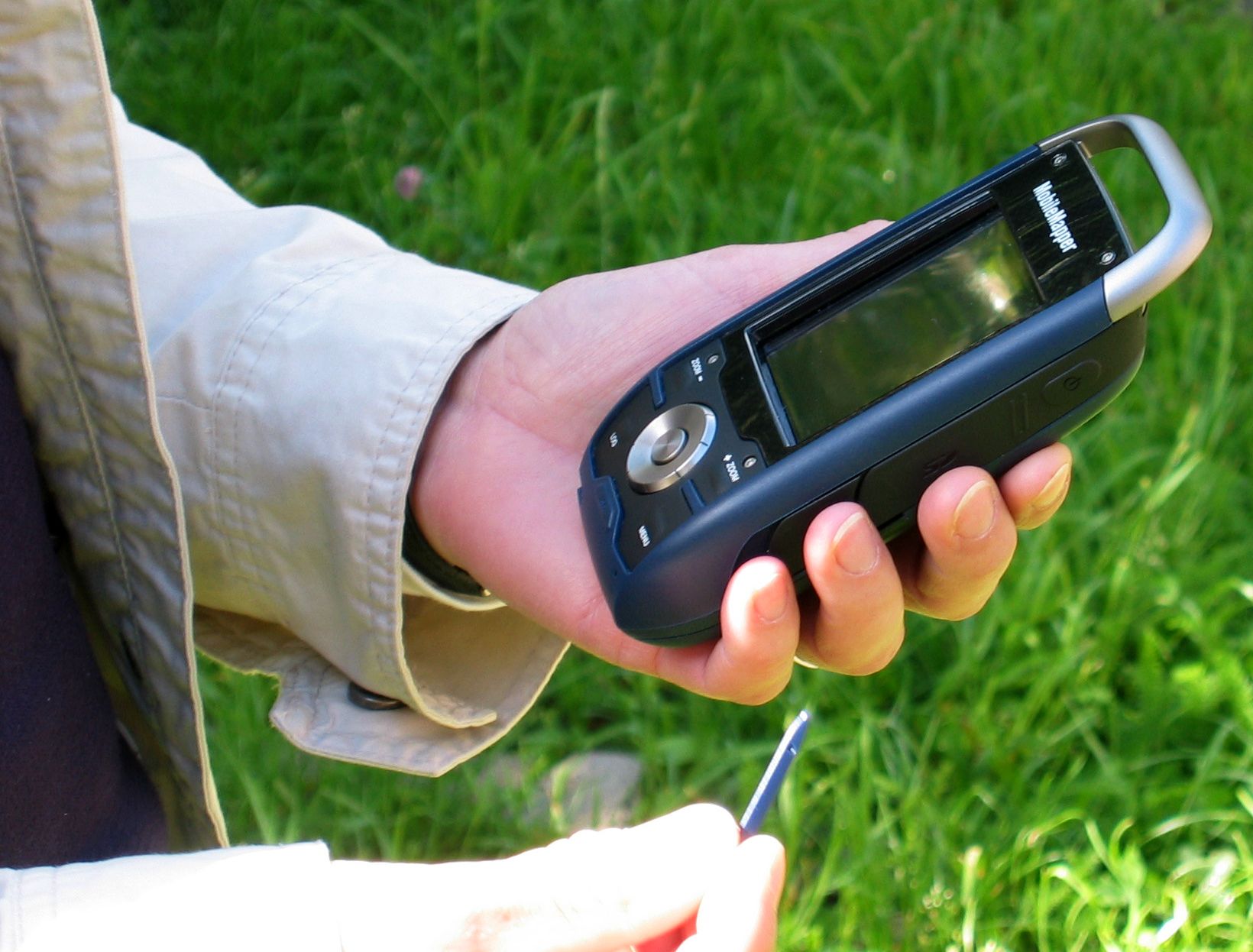 |
Data collection Data entry
Categories of apps
We categorise biodiversity mobile tools in four groups to highlight the main functionality of apps. Certainly some software fits more than one category, but in most cases an emphasis can be recognized.
-
Information
-
Identification
-
The classical way is to use a pure text-based dichotomous key for the determination of taxa. Depending to the content, specifically the vocabulary required of the user, this could address both the citizen scientist and the expert.
-
A more multimedia way is to use pictures or shapes of structures, either with or without descriptive text, to guide the user to the determination result. This style is most suitable for educational purposes and makes taxonomy more accessible to citizen scientists i.e. pupils and students.
-
-
Observation
-
Allrounder
The first category is purely informational. The user can search for species names and get some information and multimedia material about the species. Of course, the user has to know for what he or she is looking, just like an encyclopaedia. So, this kind of app has the functionality of a compact multimedia nature guide.
Some apps can search for species data or biodiversity information available at a defined locality i.e. to explore the place you currently are. In most cases these apps use localization by GPS or GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) to show numbers of taxa around you or distribution maps of particular species with links to further information.
| World of Birds | |
|---|---|
| Description: | Information about 1000 birds from all over the world. |
| Functionality: | Multimedia lexicon, scientific names, physiology |
| Operating system: | iOS, Android |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://android.jourist.info/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=130&Itemid=71&lang=en |
|
|
|
| Audubon Guides | |
| Description: | Audubon Guides is a series of applications each for a different taxonomic group (i.e. mammals, wildflowers, birds, trees, butterflies etc.) in North America. |
| Functionality: | Multimedia information about species, determination key, advanced search |
| Operating system: | iOS, Android |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://www.audubonguides.com/field-guides/ |
|
|
|
| Handheld Birds | |
| Description: | Multimedia information about birds with the possibility to fill in a checklist. |
| Functionality: | Pictures, range maps, taxonomic & ecological information, audio, eBird checklists and export. |
| Operating system: | iOS |
| Offline usage: | ? |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://www.handheldbirds.com/ |
|
|
|
| Botany Buddy | |
| Description: | Guide to trees and shrubs, inclusive succulents and tropical plants |
| Functionality: | Pictures, advanced search, original content, scientifically verified information, plant profiles |
| Operating system: | iOS >= 4 |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://avaimobile.com/portfolio/productivity/botany-buddy/ |
|
|
|
| Florafolio | |
| Description: | Field guide to native plants of North Eastern North America |
| Functionality: | Pictures, search, visual search by shape, color, wildlife benefit |
| Operating system: | iOS >= 4 |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://www.holimolimedia.com/florafolio/ |
This category, “determination apps”, helps users to identify certain taxa. Apps for several different groups of organisms are available, but fewer apps that combines the identification of several groups in a single key. Users interested in various groups find themselves having lots of apps to cover their range of requirements.
There are several possibilities for providing identification functions, so we define two subgroups here:
| Key to Nature project | |
|---|---|
| Description: | In this past project ongoing projects like ”Offene Naturführer” (open nature guides) and “Dryades” were founded. There are >500 identification keys that are in particular available in mobile versions. We list the past project as a proxy for all these tools. |
| Functionality: | Text- and image-based and interactive keys for plants and animals |
| Operating system: | Based on webbrowser, OS-independent |
| Offline usage: | Only for single access keys |
| Available: | free |
| Web: |
http://www.offene-naturfuehrer.de http://www.dryades.eu http://www.keytonature.eu |
|
|
|
| LeafSnap | |
| Description: | LeafSnap uses visual recognition to identify trees from pictures of their leaves. |
| Functionality: | Take and share pictures |
| Operating system: | iOS (>=4.2) |
| Offline usage: | no |
| Available: | free |
| Web: | http://leafsnap.com |
|
|
|
| iKosmos | |
| Description: | iKosmos provides a few identification tools (trees & shrubs, molluscs, songbirds). Some are also capable to record the sightings. |
| Functionality: | Multimedia identification |
| Operating system: | iOS (>=4.0) |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://www.ikosmos.org/ |
|
|
|
| MyNature Animal Tracks | |
| Description: | This tool is for identification of North American animals by their track size and shape. |
| Functionality: | Key through different categories of tracks, pictures, sounds and other information about the animals. |
| Operating system: | iOS and Android |
| Offline usage: | ? |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://www.mynatureapps.com/mynature-animal-tracks |
|
|
|
| EcoPod | |
| Description: | EcoPod is an app that provides different approaches for identification of taxa for citizen scientists to increase data quality. |
| Functionality: | Character key, image gallery, “backward” determination through use of hypothesizing,,the tool ingest SDD (Structured Descriptive Data) |
| Operating system: | Windows Mobile |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | ? |
| Web: | http://ilpubs.stanford.edu:8090/790/ |
It is very convenient to record biodiversity data electronically by comparison to taking notes in the field and typing everything into the PC later. It can be done either via simple checklists, web forms optimized for mobiles or interactive and/or multimedia features. These are summarised as “recording apps”.
For more nuanced applications, systems are available to allow the user to build an individual web form, database or even complete apps with software that serves as a “construction kit”. For these tools some basic understanding of programming is required.
recording tools:
| Encyclopedia of Life | |
|---|---|
| Description | Uploading pictures with geo-reference and taxon name and share it within Flickr. |
| Functionality | Upload pictures, GPS |
| Operating system | iOS |
| Offline usage | ? |
| Available | free |
| Web | http://www.eol.org |
|
|
|
| ObsMapp | |
| Description | A tool for recording observations based on OpenStreetMaps or Google Maps. |
| Functionality | Download several species lists, use GPS location, choice between offline and online maps |
| Operating system | Android |
| Offline usage | yes |
| Available | free |
| Web | https://market.android.com/details?id=org.obsmapp |
|
|
|
| Pocket eRelevé | |
| Description | Pocket eRelevé is a tool for recording observations based on OpenStreetMaps. You can export your data in different formats. |
| Functionality | GPS tracker, compass, export to XML, KML, CSV, GPX |
| Operating system | WindowsMobile (>=5.0) |
| Offline usage | yes |
| Available | free |
| Web | http://code.google.com/p/pocket-ereleve |
|
|
|
| iNaturalist | |
| Description | Uploading pictures of taxa. The community can help identifying the taxon. |
| Functionality | Take and share pictures, use GPS position, forum determination |
| Operating system | iOS (>=3.1) |
| Offline usage | yes |
| Available | free |
| Web | http://www.inaturalist.org |
|
|
|
| ArtenFinder | |
| Description | A regional recording tool for species occurrences in the federal state of Germany Rhineland-Palatinate. |
| Functionality | List of threatened species, recording, GPS position, compass |
| Operating system | iOS |
| Offline usage | ? |
| Available | free |
| Web | http://artenfinder.rlp.de/ |
|
|
|
| DiversityMobile | |
| Description | DiversityMobile is the mobile counterpart to the software DiversityCollection, which is used to record and handle observations. |
| Functionality | Species lists, recording, GPS position |
| Operating system | WindowsMobile (>=5.0) |
| Offline usage | yes |
| Available | free |
| Web | http://www.diversitymobile.net |
|
|
|
| Nature Lister | |
| Description | With Nature Lister users can use different species lists to record their sightings and geographical data. |
| Functionality | Species lists, recording, data export, data summary/statistics, internet search |
| Operating system | Android (>=2.2) |
| Offline usage | yes |
| Available | commercial |
| Web | http://www.wildlife.co.uk |
|
|
|
| Mobile Birder | |
| Description | Mobile Birder is for recording bird observations with location, date, taxonomy and identification confidence. |
| Functionality | Usage of a built in database, export, backup, automatic taxonomy creation, additional information |
| Operating system | WindowsMobile (>=5) |
| Offline usage | yes |
| Available | free |
| Web | http://www.ticklistsoftware.co.uk/Mobile_Birder_For_Windows_Pocket_PC.html |
construction tools:
| ODK Collect | |
|---|---|
| Description: | This tool can be used for building forms to collect biodiversity data. It supports almost every data type that smartphones support. The data are stored in a separate database on the device (temporarily) and on a server permanently. |
| Functionality: | Different data types: text, location, pictures, video, barcodes, audio etc.; build forms, save and fill in forms |
| Operating system: | Android (>=1.5) |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | free |
| Web: | http://www.opendatakit.org |
|
|
|
| ArcPad | |
| Description: | A tool from ESRI as a kind of mobile ArcGIS for GIS functionality and recording data. It is fully customizable with the desktop application ArcPad Studio. |
| Functionality: | GIS, data entry, user or project specific form can be built on PC |
| Operating system: | iOS, WindowsMobile, Android (beta) |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://esri.de/products/arcgis/arcpad |
|
|
|
| CyberTracker | |
| Description: | It allows to adapt an application, design a database for field guides and taxonomic keys. |
| Functionality: | Customization, export: XLS, XML, SHP, CSV |
| Operating system: | PalmOS or Windows (Mobile/CE) |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | free |
| Web: | http://www.cybertracker.org |
As mentioned above, some apps fit more than one of the former three categories and are multi-functional tools that have no strong focus on one particular aspect, but offer several functions in equal strength. It is important to stress that the definition of this category refers only to the functional, not to the taxonomic scope. Although there are applications that offer information, identification and recording functions for different taxa (i.e. Project Noah, Animals+plants), it is not required for being categorized in this group. So their might be “allrounders” only for birds (i.e. Roberts VII Multimedia PDA Edition).
| Project Noah | |
|---|---|
| Description: | Uploading pictures of taxa. The community can help to identify the taxon. |
| Functionality: | Take and share pictures, use GPS position, forum determination, accomplish missions |
| Operating system: | Android and iOS |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | free |
| Web: | http://www.projectnoah.org |
|
|
|
| Anymals+plants | |
| Description: | With Anymals+plants you can record and share any taxon, see what was found around you and get information and pictures about each taxon from wikipedia.org |
| Functionality: | Species lists, use GPS position, recording, distribution, taxon filter |
| Operating system: | Android (iOS and WindowsMobile planned) |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | free |
| Web: | http://www.anymals.org |
|
|
|
| Biodiversity Snapshot | |
| Description: | Biodiversity Snapshot is an education tool for determination of taxa, recording and presenting observations. |
| Functionality: | Field guide, customizable |
| Operating system: | iOS and Android |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | free |
| Web: | www.biodiversitysnapshots.net.au |
|
|
|
| Roberts VII Multimedia PDA Edition | |
| Description: | Electronic field guide to bird of South Africa with personal lists including sighting details |
| Functionality: | field guide, identification, interactive map, GPS, photos, sounds |
| Operating system: | Windows Mobile (iOS and Android planned) |
| Offline usage: | yes |
| Available: | commercial |
| Web: | http://www.sabirding.co.za |
Discussion
A large amount of software for mobile devices is available for use in the context of biodiversity. Our list of biodiversity apps was not intended to be comprehensive, as there are so many other applications that match our categories. Nevertheless, one can see from the listed apps that there is a great deal of choice for their combination of smartphone, taxonomic expertise or interests and their location. The diversity of specific applications for biodiversity (citizen) science is so high and so fiercely competitive, that developers need to be convinced of a market need before starting to build a new product.
The focus of most apps from the first two categories (information and identification) on a small range of popular taxa, but it means that people with a range of requirements will need an equivalent range of apps. These categories are mostly relevant to citizen scientists and this structure of having more than one app should be sufficient for them.
Comprehensive biodiversity software that satisfies all users will never exist. The category of 'allrounders' is, however, a good compromise, but changing apps generally means losing access to the data already recorded. To overcome this problem, we suggest using interfaces for connecting apps. So, if data transfer between different apps works in a general way, the user would not have to worry about using different apps for different demands. Such an approach could be easily realised (especially with construction tools) by using an international standard like the ABCD-schema or DarwinCore as a kind of uniform “language” for biodiversity apps. This would also facilitate the establishment of uniform import and export formats and consequently promote the cross-linkage as well as the data migration for both, simple and complex biodiversity data. Networks like the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) are able to press for such an approach and from which all parties can benefit.
Conclusion
The classification of biodiversity apps included the short profiles above shows that a lot of tools exist and can be applied in different scopes. Most of them address citizen scientists and can be used in schools and from interest groups, but are also able to satisfy the demand of professional scientists. The linkage of different applications has to be encouraged to reinforce the usability of the high potential this mobile software section has as a whole.
For scientists smartphone apps can simplify the acquisition of data. For citizen scientists these apps are informative, funny and bring the subject of biodiversity into people's daily routine.